The Ministry of Communication and Information Technology is a key government body in Tanzania. It oversees a number of Government Institutions responsible for implementing policy, regulating services, deploying infrastructure, and promoting digital inclusion.
Key Institutions under the Ministry, Their Duties & Responsibilities, and Achievements
Tanzania Communications Regulatory Authority (TCRA)
Duties & Responsibilities
- Regulate electronic communications, broadcasting, and postal sectors
- Manage licensing, standards, and enforcement (spectrum management, equipment standards, tariffs, and service quality)
- Protect consumers, promote competition, and ensure service availability for rural, low-income, or disadvantaged users
Achievements
- Expanded regulation of broadband and improved service quality standards
- Rolled out the National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB) connecting towns and public offices
- Developed a postcode and physical addressing system
- Established digital clubs in schools to promote ICT skills
ICT Commission (ICTC)
Duties & Responsibilities
- Drive digital transformation and foster an ICT-enabled knowledge society
- Promote ICT investment and professional registration
- Build capacity in ICT research and standards
- Enforce ICT infrastructure programmes and regulations
Achievements
- Implemented national ICT professional registration and development programmes
- Supported forums on cyber security, AI, and digital innovations
- Contributed to the National Digital Economy Strategic Framework (2024-2034)
Universal Communications Service Access Fund (UCSAF)
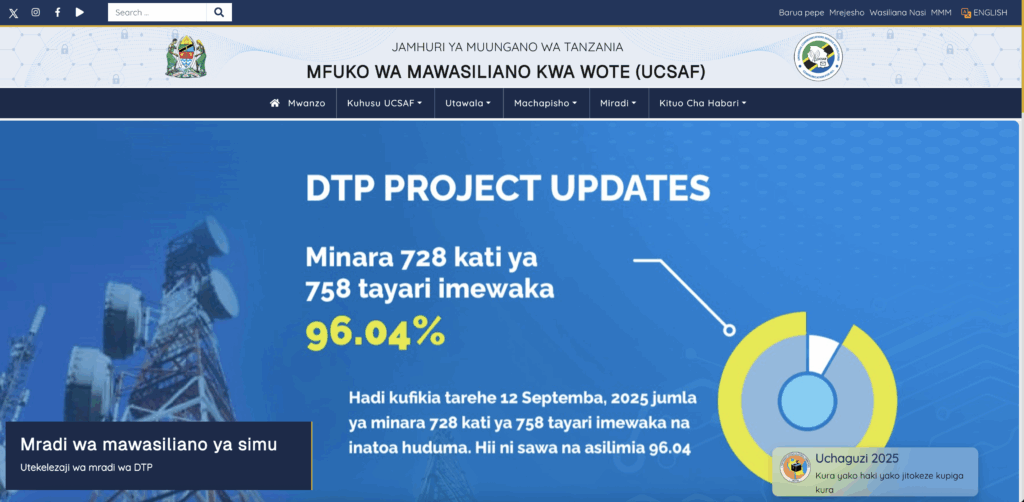
Duties & Responsibilities
- Promote universal access to communication services in underserved areas
- Provide subsidies and incentives to extend telecom infrastructure (e.g. towers)
- Collaborate with private sector to overcome economic barriers in rural connectivity
Achievements
- Constructed 304 telecom towers in 291 wards between July 2022 and June 2023, benefiting 3.3 million citizens
- Expanded service access to many rural and remote communities
e-Government Authority (eGA)

Duties & Responsibilities
- Oversee implementation of the e-Government Act (2019)
- Coordinate, monitor, and promote delivery of government digital services
- Ensure digital platforms are interoperable, standardized, and secure
Achievements
- Digitalised numerous government functions for efficient service delivery
- Built capacity in public institutions for digital transformation
- Key player in the World Bank–supported Digital Tanzania projects
Tanzania Posts Corporation (Posta)

Duties & Responsibilities
- Provide postal services (letters, parcels, EMS, courier) across Tanzania
- Offer financial services in rural areas, acting as an agent for utility collections and government payments
Achievements
- Maintained nationwide postal reach, including rural and remote areas
- Developed the 2022-2026 Strategic Business Plan to modernize postal, courier, and logistics services
Tanzania Telecommunications Corporation (TTCL)
Duties & Responsibilities
- Provide telecommunications services (fixed line, mobile, broadband, and transmission)
- Manage and operate strategic national backbone infrastructure
- Ensure secure, reliable, and commercially viable telecom services
Achievements
- Operates strategic telecom infrastructure backbone
- Plays a major role in the National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB)
- Adapted services to compete in mobile and internet markets
Overall Achievements of the Sector
Some of the cross-institutional achievements under the Ministry of Communication and Information Technology:
- Expansion of broadband and ICT infrastructure
The National ICT Broadband Backbone (NICTBB) has been rolled out to connect major towns and numerous public offices. - Legal and regulatory framework updating
Laws such as the Electronic and Postal Communications Act, Universal Communications Service Access Act, the e-Government Act, and policies like the National ICT Policy 2016 have been enacted or revised to reflect digital transformation needs. - Digital inclusion & rural access
UCSAF’s deployment of communication infrastructure in rural wards; programs to set up digital clubs in schools; services extended to low income and remote areas. - E-Government roll outs
Many public services are increasingly accessible electronically. Government institutions are implementing digital platforms, and eGA plays a strong coordinating role. - Institutional strengthening & professionalisation
- ICT Commission’s work to register ICT professionals, set standards; TCRA’s oversight and enforcement; TTCL’s re-establishment as a government owned strategic infrastructure provider.